Cyanuric acid
| Cyanuric acid | |
|---|---|
|
1,3,5-Triazinane-2,4,6-trione |
|
|
Other names
1,3,5-Triazinetriol; s-Triazinetriol; 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione; s-Triazinetrione; Tricarbimide; Isocyanuric acid; Seudocyanuric acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 108-80-5 |
| PubChem | 7956 |
| ChemSpider | 7668 |
| KEGG | C06554 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17696 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL243087 |
| RTECS number | XZ1800000 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C3H3N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 129.07 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting point |
decomp. 320–360 ºC |
| Solubility in water | 0.27 g/100 ml (25 ºC) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | ICSC 1313 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related triazines | Cyanuric fluoride Cyanuric chloride |
| (verify) (what is: /?) Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references | |
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleaches, disinfectants, and herbicides. In 1997, worldwide production was 160 million kilograms.[1]
Contents |
Properties and synthesis
Properties
Cyanuric acid is the cyclic trimer of the elusive species cyanic acid, HOCN. The two structures shown in the infobox readily interconvert; that is, they are tautomers. However, mixture with melamine forms melamine cyanurate, which locks cyanuric acid in the tri-keto tautomer and makes melamine cyanurate insoluble in water. The triol tautomer, which may have aromatic character, predominates in solution. The hydroxyl (-OH) groups assume phenolic character. Deprotonation with base affords a series of cyanurate salts:
- [C(O)NH]3
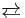 [C(O)NH]2[C(O)N]- + H+ (Ka = 10−7)
[C(O)NH]2[C(O)N]- + H+ (Ka = 10−7) - [C(O)NH]2[C(O)N]-
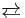 [C(O)NH][C(O)N]22- + H+ (Ka = 10−11)
[C(O)NH][C(O)N]22- + H+ (Ka = 10−11) - [C(O)NH][C(O)N]22-
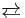 [C(O)N]33- + H+ (Ka = 10−14)
[C(O)N]33- + H+ (Ka = 10−14)
Synthesis
Cyanuric acid (CYA) was first synthesized by Friedrich Wöhler in 1829 by the thermal decomposition of urea and uric acid.[2] The current industrial route to CYA entails the thermal decomposition of urea, with release of ammonia. The conversion commences at approximately 175 °C:[1]
- 3 H2N-CO-NH2 → [C(O)NH]3 + 3 NH3
CYA crystallizes from water as the dihydrate.
Cyanuric acid can be produced by hydrolysis of crude or waste melamine followed by crystallization. Acid waste streams from plants producing these materials contain cyanuric acid and on occasion, dissolved amino-substituted triazines, namely, ammeline, ammelide, and melamine. In one method, an ammonium sulfate solution is heated to the "boil" and treated with a stoichiometric amount of melamine, by which means the cyanuric acid present precipitates as melamine-cyanuric acid complex. The various waste streams containing cyanuric acid and amino-substituted triazines may be combined for disposal and during upset conditions, undissolved cyanuric acid may be present in the waste streams. [3][4]
Intermediates and impurities
Intermediates in the dehydration include both isocyanic acid, biuret, and triuret:
- H2N-CO-NH2 → HNCO + NH3
- H2N-CO-NH2 + HNCO → H2N-CO-NH-CO-NH2
- H2N-CO-NH-CO-NH2 + HNCO → H2N-CO-NH-CO-NH-CO-NH2
One impurity in the production of CYA is ammelide, especially as the reaction temperature exceeds 190 °C: 3 H2N-CO-NH-CO-NH2 → [C(O)]2(CNH2)(NH)2N + 2 NH3 + H2O The first appearance of ammelamide occurs prior to 225 °C and is suspected also to occur from decomposition of biuret but is produced at a slower rate than that of CYA.
Melamine, [C(NH2)N]3, formation occurs between 325 and 350 °C and only in very small quantities.[5]
Applications
Precursors to chlorinated cyanurates
Cyanuric acid is mainly used as a precursor to N-chlorinated cyanurates, which are used to disinfect water. The dichloro derivative is prepared by direct chlorination:
- [C(O)NH]3 + 2 Cl2 + 2 NaOH → [C(O)NCl]2[C(O)NH]
This species is typically converted to its sodium salt, sodium dichloro-s-triazinetrione. Further chlorination gives trichloroisocyanuric acid, [C(O)NCl]3. These N-chloro compounds serve as disinfectants and algicides for swimming pool water.[1] It stabilizes the chlorine in the pool and prevents the chlorine from being quickly consumed by sunlight.
Precursors to crosslinking agents
Because of their trifunctionality, CYA is a precursor to crosslinking agents, especially for polyurethane resins.
Analysis
Testing for cyanuric acid concentration is commonly done with a turbidometric test, which uses a reagent, melamine, to precipitate the cyanuric acid. The relative turbidity of the reacted sample quantifies the CYA concentration. Referenced in 1957.[6] This test works because melamine combines with the cyanuric acid in the water to form a fine, insoluble, white precipitate (melamine cyanurate) that causes the water to cloud in proportion to the amount of cyanuric acid in it. More recently, a sensitive method has been developed for analysis of cyanuric acid in urine. [7]
Animal feed
FDA permits a certain amount of cyanuric acid to be present in some non-protein nitrogen (NPN) additives used in animal feed and drinking water.[8] Cyanuric acid has been used as NPN. For example, Archer Daniels Midland manufactures an NPN supplement for cattle, which contains biuret, triuret, cyanuric acid and urea.[9]
2007 pet food recalls
Cyanuric acid is implicated in connection to the 2007 pet food recalls, the contamination and wide recall of many brands of cat and dog foods beginning in March 2007. Research has found evidence that cyanuric acid, a constituent of urine, together with melamine forms poorly soluble crystals which can cause renal failure (see Analysis section above).
Safety
Cyanuric acid is classified as "essentially nontoxic".[1] The 50% oral median lethal dose (LD50) is 7700 mg/kg in rats.[10]
However, when cyanuric acid is administered together with melamine (which by itself is another low-toxicity substance), they may form extremely insoluble crystals,[11] leading to formation of kidney stones and potentially causing kidney failure and death -- as evidenced in dogs and cats during the 2007 pet food contamination and in children during the 2008 Chinese milk scandal cases.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Klaus Huthmacher, Dieter Most "Cyanuric Acid and Cyanuric Chloride" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. ISBN 10.1002/14356007.a08 191
- ^ Wöhler, F. On the decomposition of urea and uric acid at high temperature. Ann Phys Chemie 1829 15:619-30
- ^ "Process for preparing pure cyanuric acid". July 14, 1981. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4278794.html. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ "High pressure thermal hydrolysis process to decompose triazines in acid waste streams". March 22, 1977. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4013757.html. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- ^ Shaber, Peter M. et al. "Study of the thermal decomposition of urea (pyrolysis) reaction and importance to cyanuric acid production," American Laboratory, August 1999: 13-21[1]
- ^ "Merck Turbidity Test". Merck. June 6, 2003. http://www.merckserono.net/servlet/PB/menu/1169010/index.html. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ Panuwet P, Wade EL, Nguyen JV, Montesano MA, Needham LL, Barr DB. Quantification of cyanuric acid residue in human urine using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2010 878(28):2916-2922.
- ^ "21CFR573.220 Feed-grade biuret". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. April 1, 2006. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfCFR/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=573.220. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "Roughage Buster Plus: ingredients". Archer Daniels Midland. http://www.admani.com/alliancebeef/RoughageBusterPlus.htm. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ U.S. Food and Drug Administration, "Interim Melamine and Analogues Safety/Risk Assessment; Availability", Federal Register: May 30, 2007 (Volume 72, Number 103). Accessed 2008-09-27.
- ^ "Melamine and Cyanuric Acid Interaction May Play Part in Illness and Death from Recalled Pet Food", American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), Press Release, May 1, 2007. Accessed 2008-09-27.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 1313
- Oregon Veterinary Medical Association (OVMA) Pet Food Contamination Page - News & developments updated regularly